
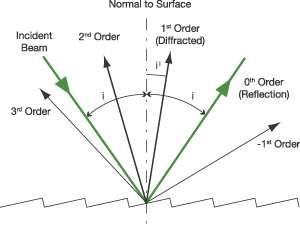
Default values will be entered for unspecified parameters, but all values may be changed. n is the diffraction order and says by how many wavelengths the wavefront shifts between incidence and scattering. The data will not be forced to be consistent until you click on a quantity to calculate. This leads to The Grating Equation: (1) n d ( sin + sin ) with the sign convention as noted. This calculation is designed to allow you to enter data and then click on the quantity you wish to calculate in the active formula above. This resolvance implies that the wavelength resolution is If N = slits are illuminated, then the resolvance R =. The resolvance of such a grating depends upon how many slits are actually covered by the incident light source i.e., if you can cover more slits, you get a higher resolution in the projected spectrum. The displacement from the centerline for maximum intensity will be A diffraction grating is made by making many parallel scratches on the surface of a flat piece of some transparent material. Projected on a screen at distance D = cm, The slit separation is d = micrometers = x10^ m.įor incident light wavelength λ = nm at order m = , Often gratings are described by the frequency of grating lines instead of the period, where f (in lines/mm) is equal to 10 6 / (for in nm). For a given angle of incidence,, it gives the angle of diffraction m for each order m for which a solution to (1) exists. However, angular separation of the maxima is generally much greater because the slit spacing is so small for a diffraction grating.ĭisplacement y = (Order m x Wavelength x Distance D)/( slit separation d)įor a diffraction grating with lines/mm = lines/inch, (1) This is the well-known Grating Equation. The condition for maximum intensity is the same as that for a double slit. A diffraction grating is the tool of choice for separating the colors in incident light.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
